Przygotowanie elementów podczas produkcji do cynkowania ogniowego
1. WYMIARY WANNY CYNKOWNICZEJ
 Przed przystąpieniem do wykonawstwa elementów stalowych, które mają być ocynkowane ogniowo należy najpierw sprawdzić wymiary wanny cynkowniczej, w której elementy mają zostać zanurzone!
Przed przystąpieniem do wykonawstwa elementów stalowych, które mają być ocynkowane ogniowo należy najpierw sprawdzić wymiary wanny cynkowniczej, w której elementy mają zostać zanurzone!
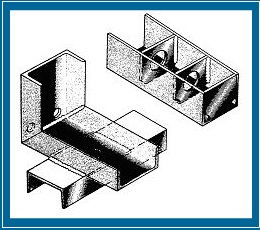
Należy w miarę możliwości unikać konstruowania elementów przestrzennych, które są nie tylko kłopotliwe podczas transportowania, ale również podczas cynkowania. Elementy płaskie cynkuje się łatwiej uzyskując lepszą jakość powłoki (mniej obróbki-czyszczenia) oraz lepszą kategorię cenową!
2. NACIĘCIA NAROŻNIKÓW ORAZ OTWORY TECHNOLOGICZNE
Wykonać nacięcia w narożach oraz otwory rozładowujące ciśnienie przy nakładkach
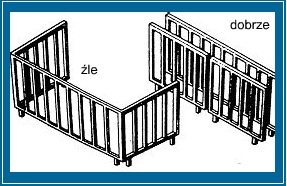
3. UNIKAĆ STOSOWANIA BLACH O DUŻYCH POWIERZCHNIACH PŁASKICH MOGĄCYCH SIĘ ZWICHROWAĆ
 Jeżeli nie jest możliwe uniknięcie stosowania blach o dużych powierzchniach, wówczas należy zastosować niżej podane rozwiązania konstrukcyjne celem zwiększenia stabilności konstrukcji:
Jeżeli nie jest możliwe uniknięcie stosowania blach o dużych powierzchniach, wówczas należy zastosować niżej podane rozwiązania konstrukcyjne celem zwiększenia stabilności konstrukcji:
- zaokrąglić krawędzie
- wykonać rowki usztywniające na powierzchniach płyt
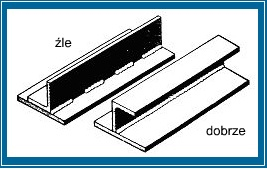
4. UNIKAĆ POŁĄCZEŃ NAKŁADKOWYCH
5. WYKONYWAĆ SZCZELNE SPAWY
Z nieszczelnych spawów mogą wypływać resztki kwasów lub topnika używanych w procesie przygotowania powierzchni
przed cynkowaniem
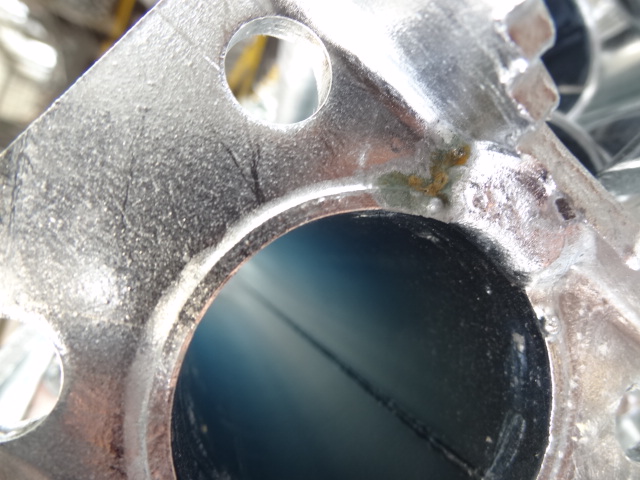
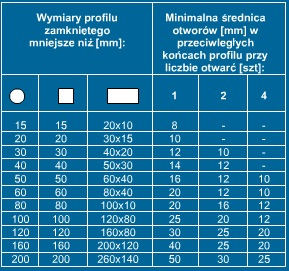
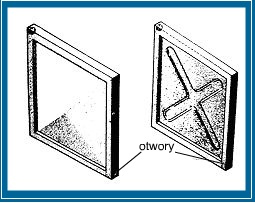
6. WYKONAĆ DOSTATECZNĄ ILOŚĆ ORAZ ZACHOWAĆ ZALECANE ŚREDNICE OTWORÓW
7. NIE UŻYWAĆ SPRAYU SPAWALNICZEGO, FARB ORAZ USUNĄĆ SZLAKĘ PO SPAWANIU
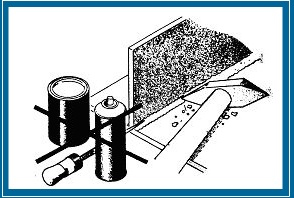 Powierzchnie elementów przeznaczonych do cynkowania ogniowego powinny być wolne od zanieczyszczeń
Powierzchnie elementów przeznaczonych do cynkowania ogniowego powinny być wolne od zanieczyszczeń
w postaci farb olejnych, primerów, pozostałości po sprayu spawalniczym, ponieważ nie można ich usunąć podczas standardowego procesu przygotowania chemicznego. Miejsca te pozostaną nieocynkowane
(czarne plamy) i są narażone na korozję.
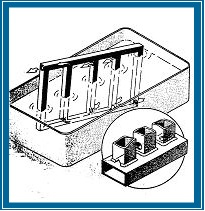
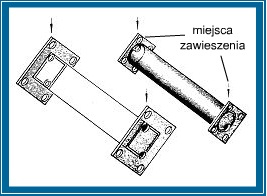
8. UMOŻLIWIĆ ZAWIESZENIE ELEMENTÓW
Otwory umożliwiające wpłynięcie cynku do profili zamkniętych oraz otwory odpowietrzające należy w miarę możliwości wykonać pod otworami umożliwiającymi zawieszenie.
9. NORMY
- należy przestrzegać normy PN EN ISO 1461 dotyczącej cynkowania ogniowego jednostkowego
- cynkować ogniowo można wszystkie gatunki stali zawarte w normie DIN 17100 oraz PN 88/H-84020 i PN-89/H-840118
Stale o krytycznej zawartości krzemu i fosforu sprzyjają tworzeniu się grubej powierzchni cynku oraz szarzeją.
10. WADY SPOWODOWANE NIEWŁAŚCIWYM PRZYGOTOWANIEM ELEMENTÓW DO CYNKOWANIA
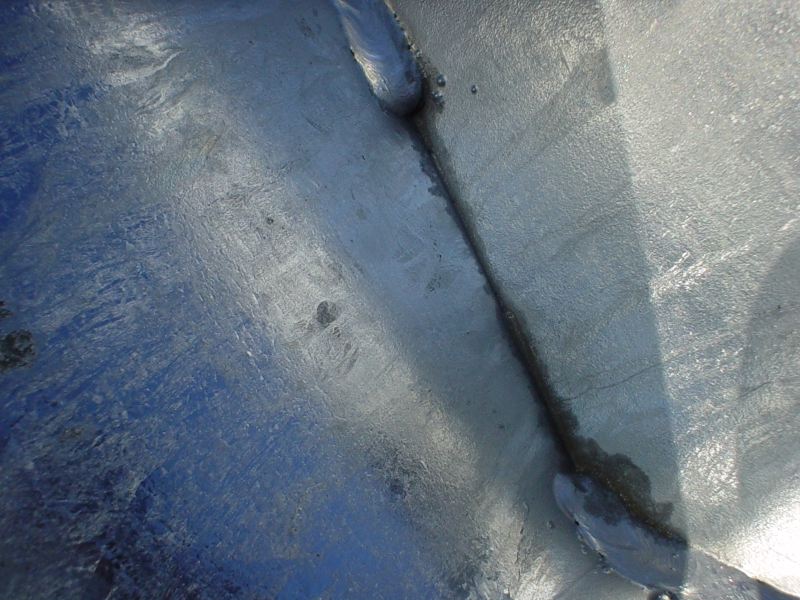 nieszczelne spawy |
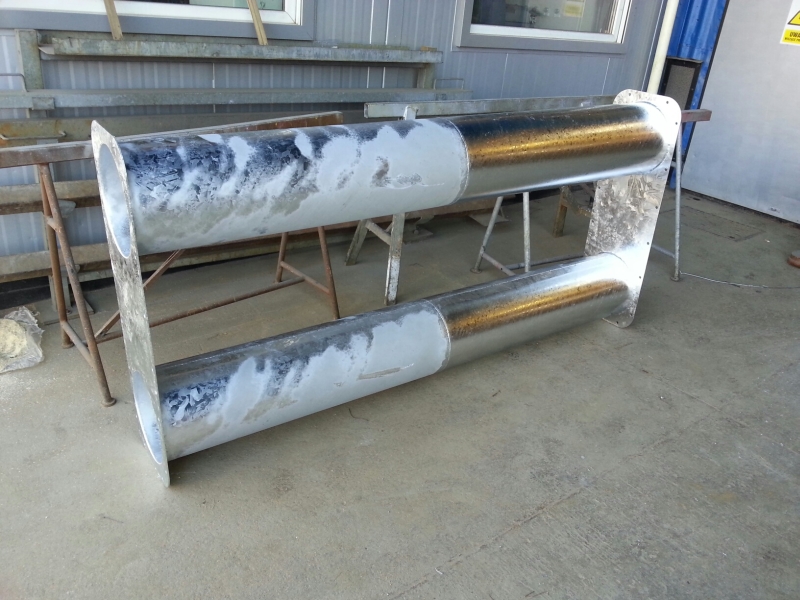 stal od dwóch dostawców |
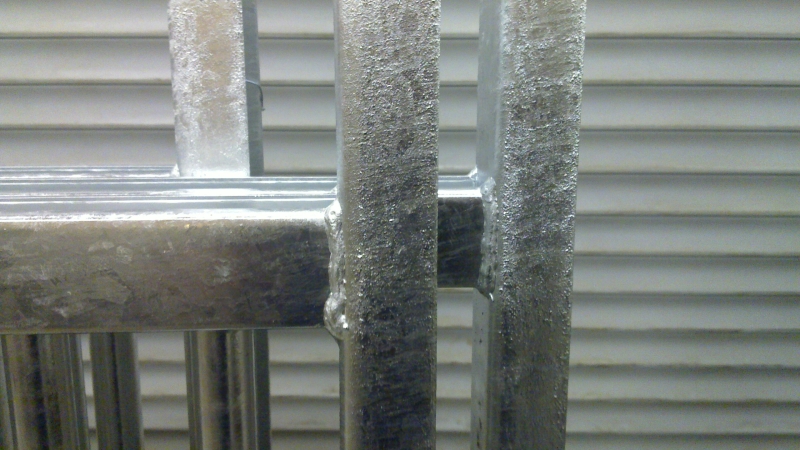 zbyt duża zawartość krzemu |
 nieoczyszczona zgorzelina spawalnicza |
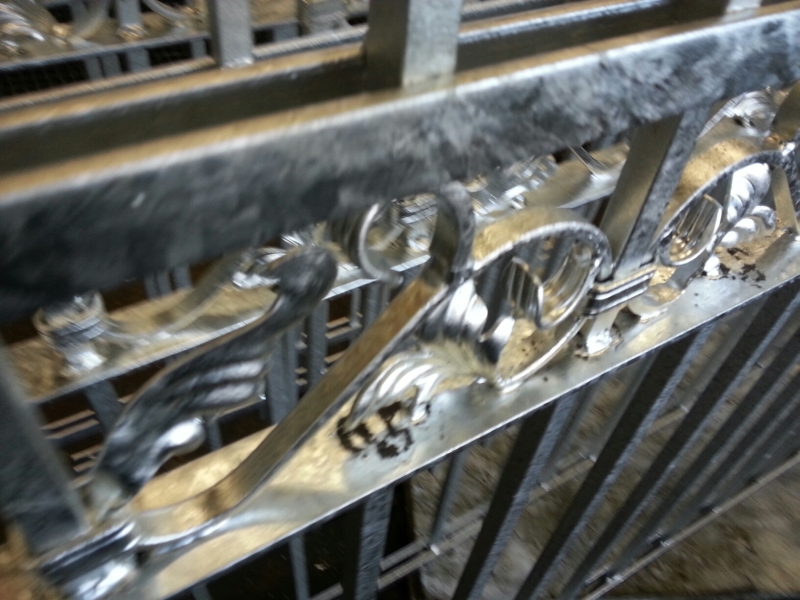 znakowanie stali markerem |
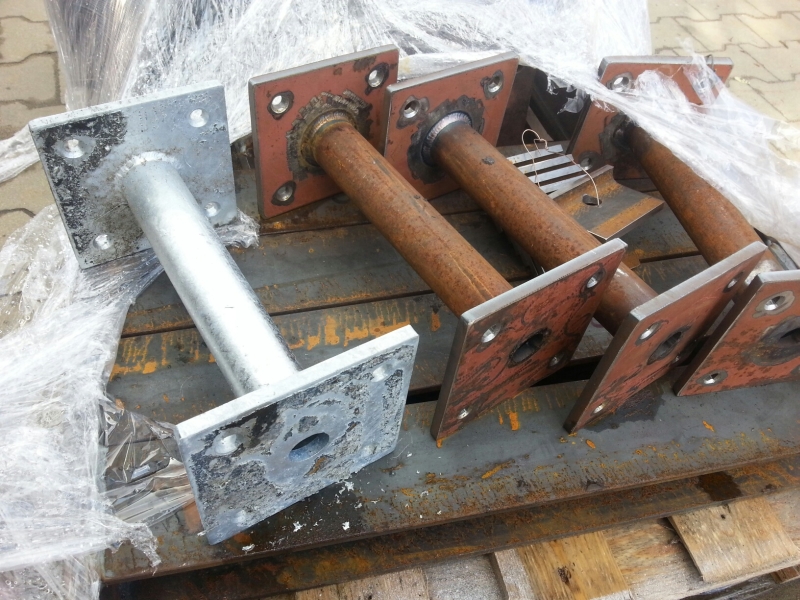 element pomalowany farbą |